In this post we are going to describe in general way the new and main features of the latest Veeam Data Platform 12.1 release.
Without a doubt, the main skill added to the software engine is Malware Detection, that is the ability to detect and identify cyber attacks, by leveraging three new technologies:
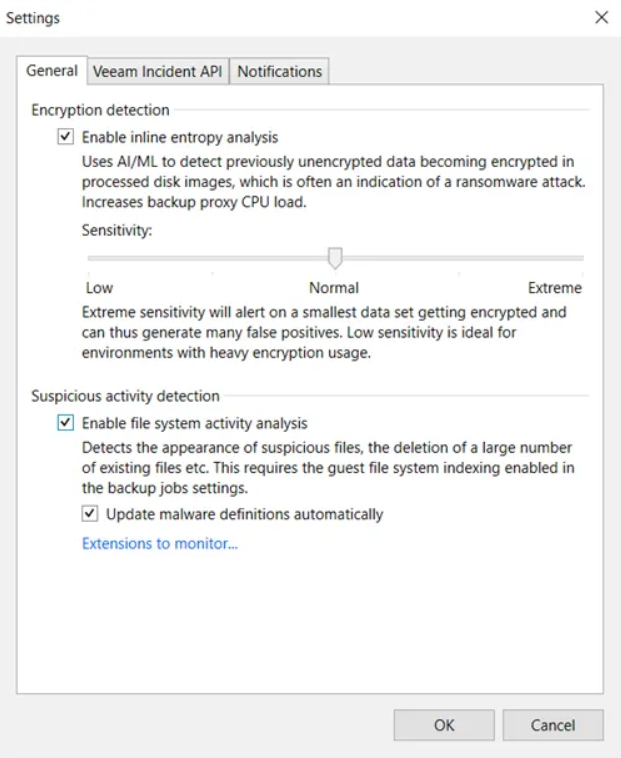
Inline malware detection: based on ML (Machine Learning) methods, it performs real-time, low-impact analysis of the backup stream to detect possible encryption activities taking place on the data
Suspicious file system activity detection: searches, by indexing the guest file system, for suspicious files, such as known malware extensions, ransom notes, etc.; it also analyzes file system activity, comparing previous indexes in order to detect suspicious changes, such as on the number and type of files present
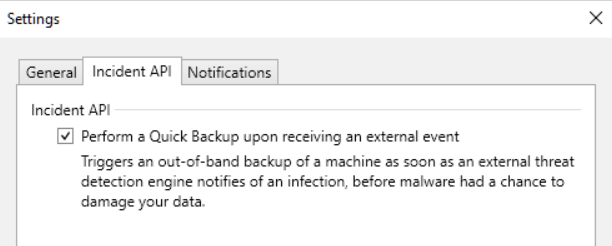
Early threat detection: takes advantage of the Veeam Incident API to receive notifications from EDR/XDR about possible infections taking place on servers in our infrastructure; this allows Veeam B&R to mark corresponding subsequent backups as compromised; it is also possible to trigger an automatic backup to the infected server as a response to this event, so that we try to secure as many files as possible before the encryption task is completed
The second important aspect concerns the ability to respond to a possible malware attack more quickly and efficiently. The features that can perform this important innovation are:
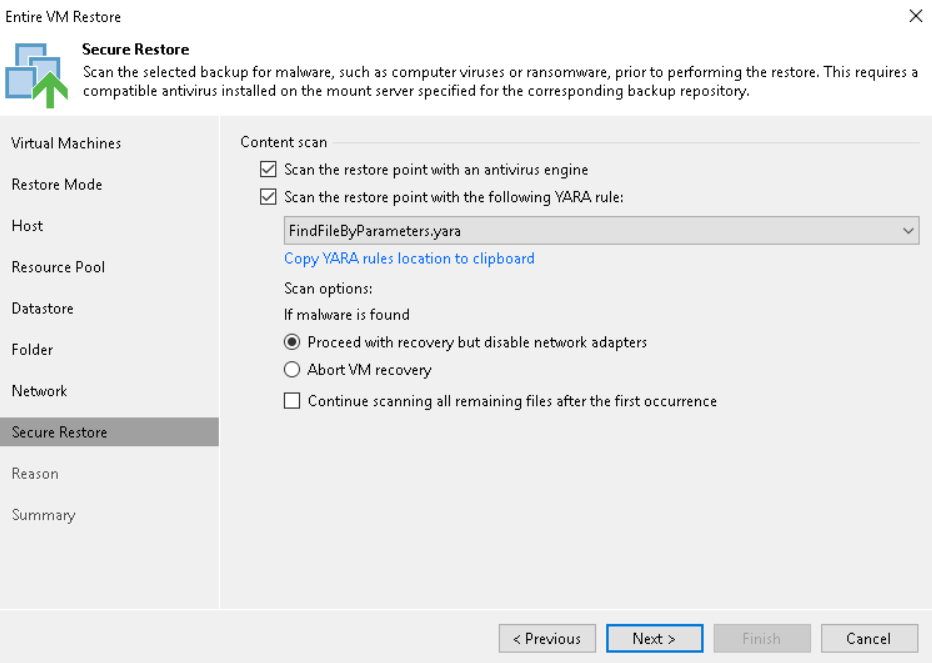
Scan backups with YARA: in addition to the classic scan with antivirus, in this version Veeam has introduced the possibility, in order to perform checks during the restore phase, to ultilize also the YARA rules, parts of code based on specific patterns depending on the type of search or the files to be found (for example, for a particular family of malware); the scan is now able to search more quickly, in a sequential or binary manner, for an non-infected backup file, speeding up the restore operations following an attack; it is also possible to use SureBackup jobs in scan-only mode (without Virtual Lab)
Avoid reinfection with threat tracking: in this new version, the software is able to detect and keep track of which backups are potentially infected, so as to avoid any restore of already compromised files; in case of false positives, an exclusion can be set manually
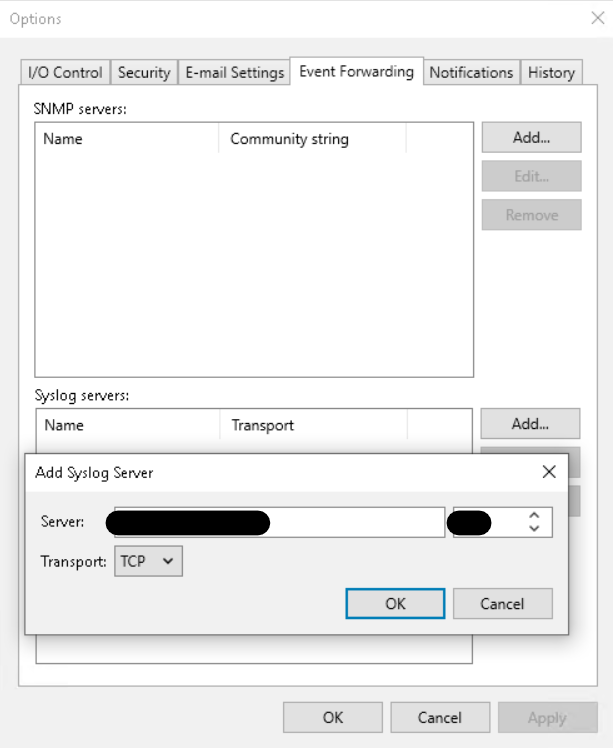
Event forwarding: with the introduction of Syslog support, Veeam is able to send any event to a SIEM of our choice, so as to trigger mechanisms to react to certain security incidents reported by the software
Finally, the security and compliance of certain operations has been improved.
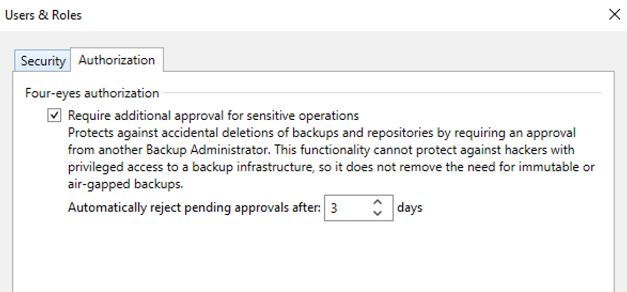
Four-eyes authorization: a setting that activates a double-check on particular sensitive operations, such as deleting a backup, a repository or adding a new Veeam Administrator, allowing to limit accidental errors or compromise attempts by a malicious user; specifically, when an admin performs one of these operations, a second admin’s approval is required within a configurable time range, after which the request is rejected
Key Management Server (KMS) integration: thanks to the integration with KMIP (Key Management Interoperability Protocol), it is now possible to use any supported KMS to perform automatic rotation of encryption keys
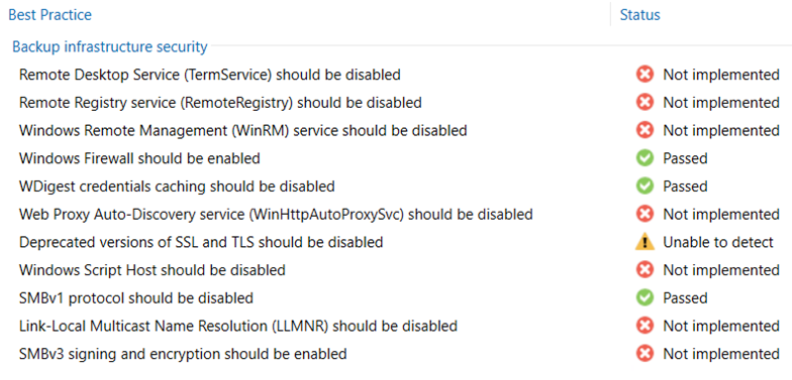
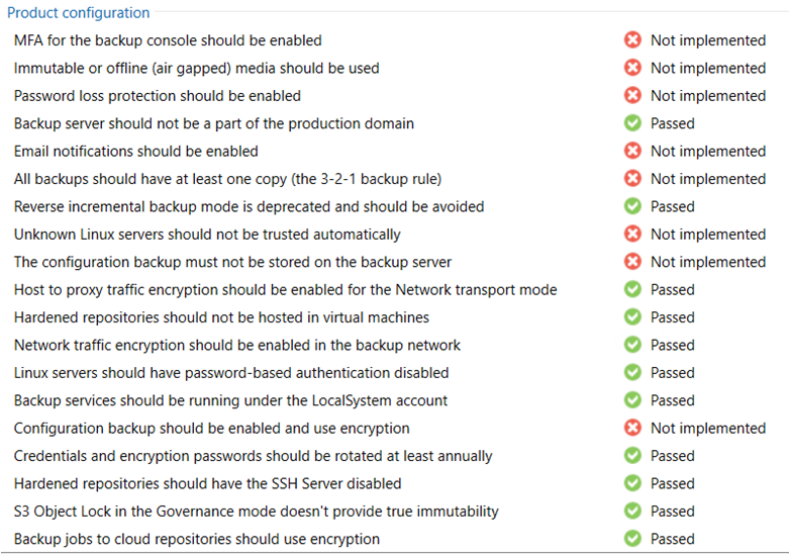
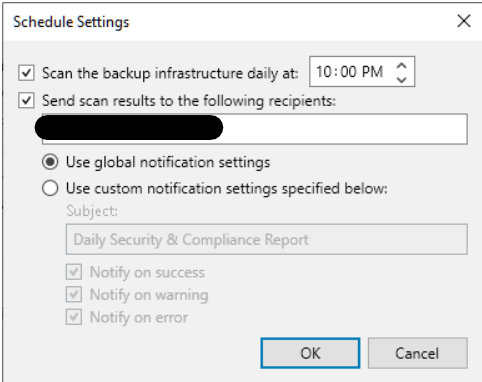
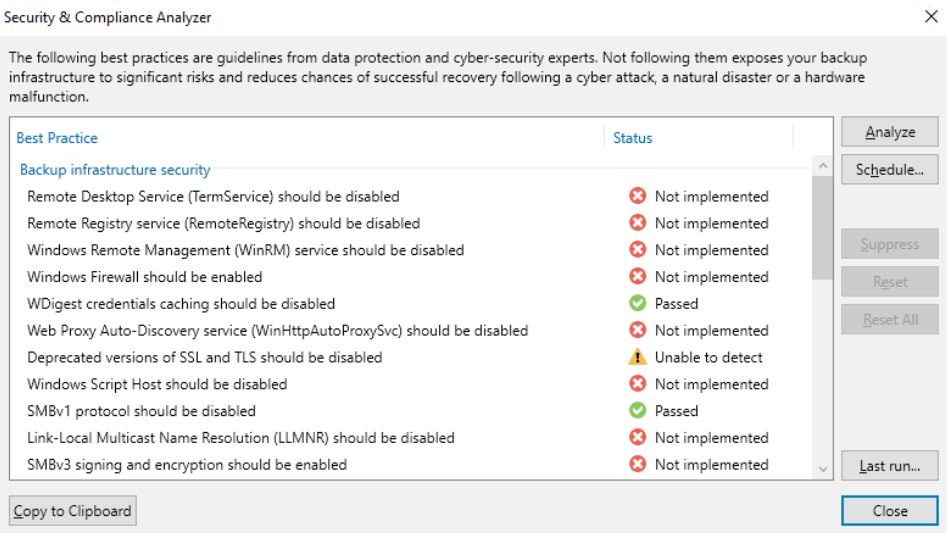
Security and compliance analyzer: a tool built into the VBR console, it allows for manual or scheduled verification of compliance with specific security baselines of our backup infrastructure, ensuring that various software best practices are being applied; it has been improved over v12, introducing many more controls, and enabling the ability to schedule a report and send it via email
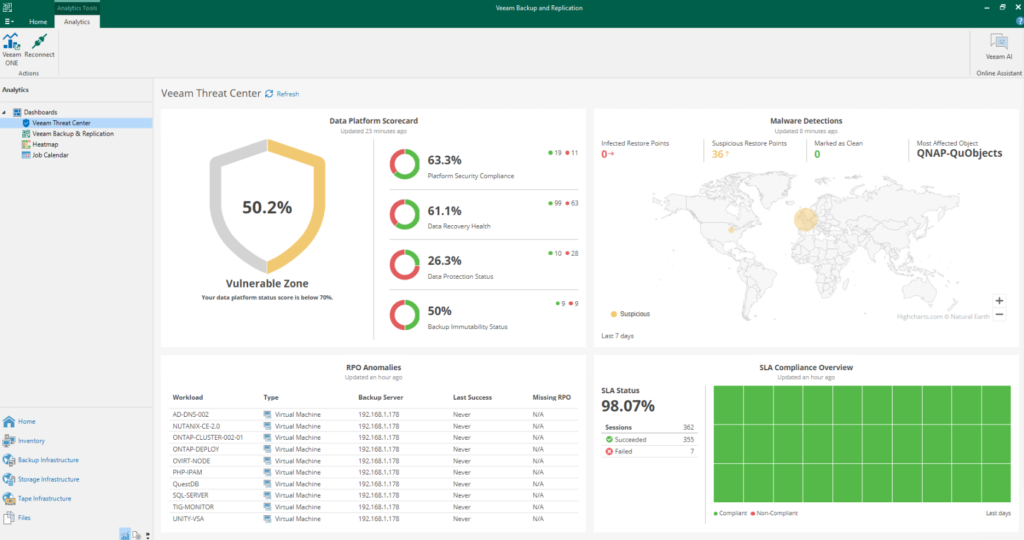
Veeam Threat Center: a specific Veeam ONE dashboard is now integrated into the VBR console, and allows us to highlight identified malicious events, possible risks and critical areas, as well as a score on the overall status of our backup infrastructure based on the implementation of various best practices recommended by the software
Other important features added are:
Object storage backup: thanks to a storage-agnostic architecture, the ability to backup object storage type sources has been included, protecting the data in our buckets, whether they are on-prem or in the cloud
CDP engine enhancement: the Veeam Continous Data Protection, which allows for the smallest RPOs for our backups, has been improved both in terms of functionality (4x number of VM-vDisks supported) and efficiency (reduced computational requirements by 2x); also introduced the ability to perform failover tests without interrupting current replicas
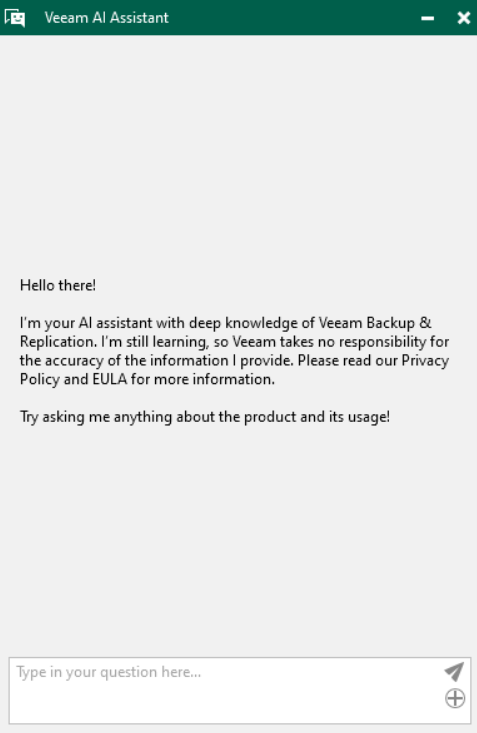
Veeam AI assistant: here within the VBR console is our “personal assistant” based on the OpenAI model, which can be used, thanks to its learning from official Veeam documentation, for help and advice on our backup infrastructure
As soon as possible, future posts will explore some of these new features individually.
For details of all the many features introduced with Veeam Data Platform 12.1 please refer to the following official document.
https://www.veeam.com/veeam_backup_12_1_whats_new_wn.pdf
Enjoy! 💚